CPU Identification
CPUID instruction
CPUID는 Intel에서 제공하는 프로세서 명령어입니다. 해당 글에서는 HyperPlatform 코드를 참조합니다.
해당 명령을 통해 현재 프로세서에 대한 식별 정보를 획득할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
CHAPTER 21
PROCESSOR IDENTIFICATION AND FEATURE DETERMINATION
When writing software intended to run on IA-32 processors, it is necessary to identify the type of processor present
in a system and the processor features that are available to an application.
호출 시 전달되는 값에 따라 다른 정보를 반환하며 해당 정보들은 EAX, EBX, ECX, EDX 레지스터를 통해 반환됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
21.1 USING THE CPUID INSTRUCTION
Use the CPUID instruction for processor identification in the Pentium M processor family, Pentium 4 processor
family, Intel Xeon processor family, P6 family, Pentium processor, and later Intel486 processors. This instruction
returns the family, model, and (for some processors) a brand string for the processor that executes the instruction.
It also indicates the features that are present in the processor and gives information about the processor’s caches
and TLB.
The ID flag (bit 21) in the EFLAGS register indicates support for the CPUID instruction. If a software procedure can
set and clear this flag, the processor executing the procedure supports the CPUID instruction. The CPUID instruction will cause the invalid opcode exception (#UD) if executed on a processor that does not support it.
To obtain processor identification information, a source operand value is placed in the EAX register to select the
type of information to be returned. When the CPUID instruction is executed, selected information is returned in the
EAX, EBX, ECX, and EDX registers. For a complete description of the CPUID instruction, tables indicating values
returned, and example code, see CPUID—CPU Identification in Chapter 3 of the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures
Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A.
CPUID 명령어는 WDK를 통해 다음과 같은 형태로 호출이 가능합니다.
아래 코드는 GitHub에 게시된 HyperPlatform 코드 중 일부입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// Tests if HyperPlatform is already installed
_Use_decl_annotations_ static bool VmpIsHyperPlatformInstalled() {
PAGED_CODE();
int cpu_info[4] = {};
__cpuid(cpu_info, 1);
const CpuFeaturesEcx cpu_features = {static_cast<ULONG_PTR>(cpu_info[2])};
if (!cpu_features.fields.not_used) {
return false;
}
__cpuid(cpu_info, kHyperVCpuidInterface);
return cpu_info[0] == 'PpyH';
}
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual에는 CPUID의 전달 값과 반환되는 정보에 대한 모든 내용들이 설명되어 있습니다.
이 중에서 01H, 40000001H을 전달했을 때 반환되는 값은 다음과 같습니다.
Initial EAX Value(01H)
Version Information (EAX)
EAX에는 Version Information이 반환됩니다.
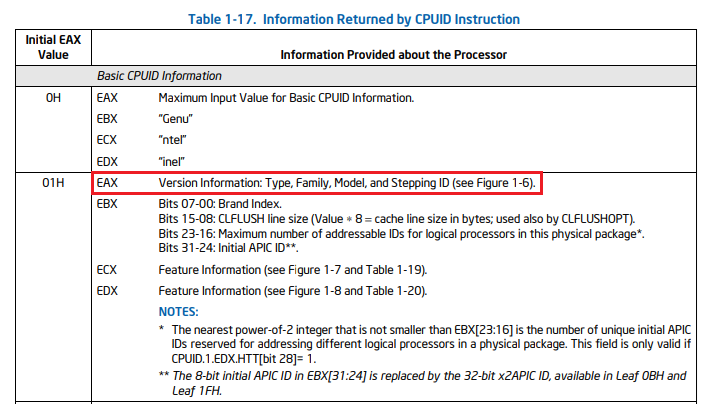
Version Information에는 CPU Model, Family, Stepping 정보가 포함되어 있습니다.
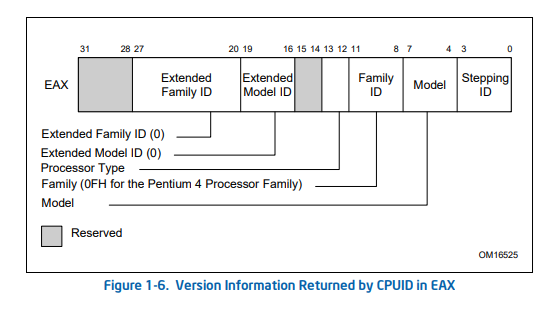
Feature Information (ECX)
ECX에는 Feature Information이 반환됩니다.
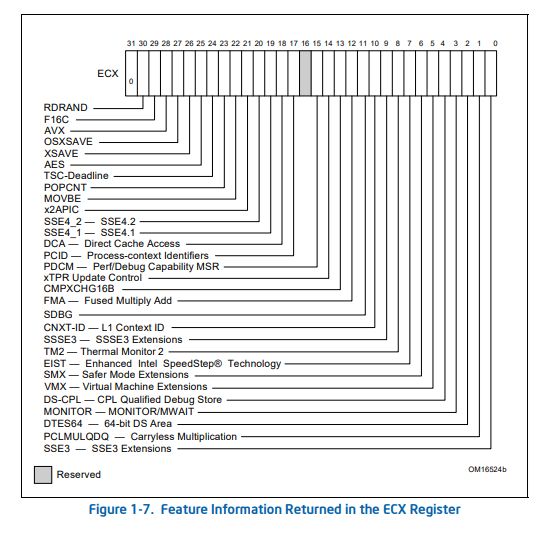
반환되는 각 정보들에 대한 상세 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
5비트에 해당되는 VMX 필드는 현재 프로세서의 VT-x 지원 여부를 나타냅니다.
31비트에 해당하는 NotUsed 필드는 HyperPlatform에서 현재 하이퍼바이저가 실행 중인지 체크하는 용도로 사용됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// Tests if HyperPlatform is already installed
_Use_decl_annotations_ static bool VmpIsHyperPlatformInstalled() {
PAGED_CODE();
int cpu_info[4] = {};
__cpuid(cpu_info, 1);
const CpuFeaturesEcx cpu_features = {static_cast<ULONG_PTR>(cpu_info[2])};
if (!cpu_features.fields.not_used) {
return false;
}
__cpuid(cpu_info, kHyperVCpuidInterface);
return cpu_info[0] == 'PpyH';
}
Intel 문서에서는 해당 값이 Reserved로 설명되는데 일부 하이퍼바이저에서는 이를 활용하여 사용하고 있는 것으로 보입니다.

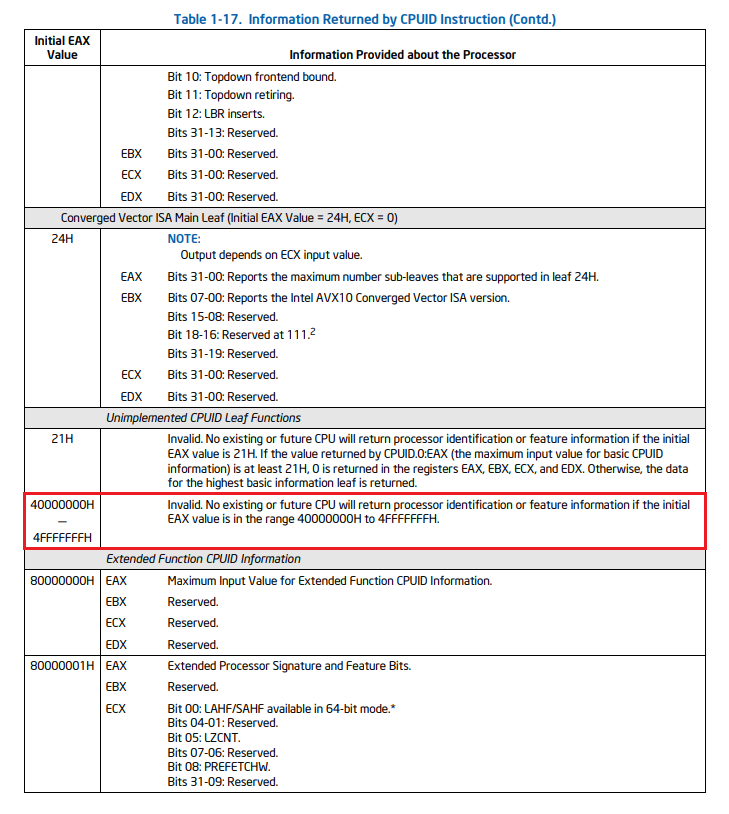
Initial EAX Value(40000000H − 4FFFFFFFH)
해당 범위 내 값은 유효하지 않습니다. 일부 하이퍼바이저에서는 이를 직접 구현하여 사용합니다.
HyperPlatform에서는 다음과 같이 정의하여 시그니처 값을 노출합니다.
1
2
3
4
/// A majority of modern hypervisors expose their signatures through CPUID with
/// this CPUID function code to indicate their existence. HyperPlatform follows
/// this convention.
static const ULONG32 kHyperVCpuidInterface = 0x40000001;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// CPUID
_Use_decl_annotations_ static void VmmpHandleCpuid(
GuestContext *guest_context) {
HYPERPLATFORM_PERFORMANCE_MEASURE_THIS_SCOPE();
unsigned int cpu_info[4] = {};
const auto function_id = static_cast<int>(guest_context->gp_regs->ax);
const auto sub_function_id = static_cast<int>(guest_context->gp_regs->cx);
__cpuidex(reinterpret_cast<int *>(cpu_info), function_id, sub_function_id);
if (function_id == 1) {
// Present existence of a hypervisor using the HypervisorPresent bit
CpuFeaturesEcx cpu_features = {static_cast<ULONG_PTR>(cpu_info[2])};
cpu_features.fields.not_used = true;
cpu_info[2] = static_cast<int>(cpu_features.all);
} else if (function_id == kHyperVCpuidInterface) {
// Leave signature of HyperPlatform onto EAX
cpu_info[0] = 'PpyH';
}
guest_context->gp_regs->ax = cpu_info[0];
guest_context->gp_regs->bx = cpu_info[1];
guest_context->gp_regs->cx = cpu_info[2];
guest_context->gp_regs->dx = cpu_info[3];
VmmpAdjustGuestInstructionPointer(guest_context);
}