Control Registers
작성중…..
Control Registers
컨트롤 레지스터는 현재 사용 중인 메모리에 대한 정보를 포함하고, 프로세서에 대한 다양한 기능들을 제어합니다.
CR0 ~ CR4 까지 전체적인 이미지는 다음과 같습니다.
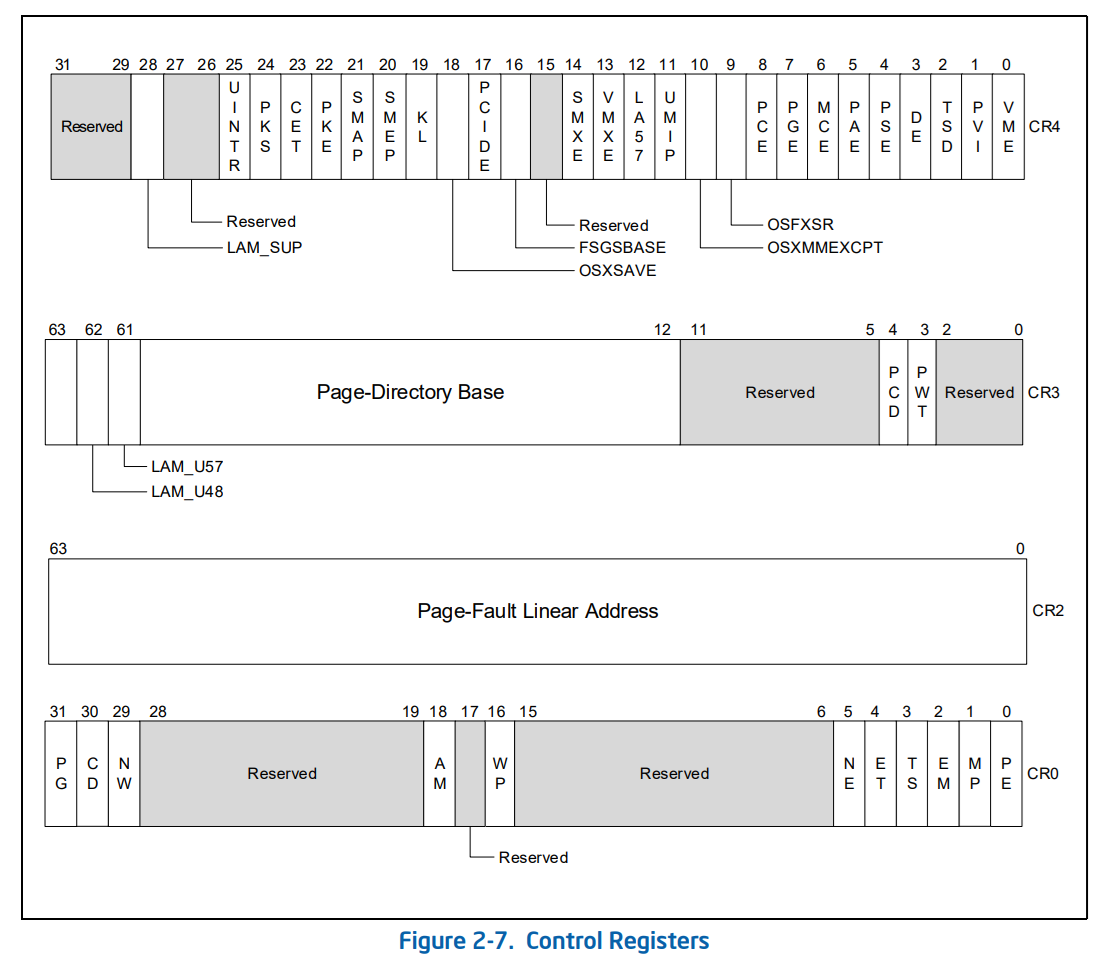
CR0
보호모드, 페이징, 캐시 등 프로세서의 기본적인 기능들을 제어합니다.
| Bit | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | PE (Protection Enable) | 보호 모드 활성화 |
| 1 | MP (Monitor Coprocessor) | x87 FPU 감시용 (TS와 연동) |
| 2 | EM (Emulation) | FPU 명령어 에뮬레이션 (1 = FPU 비활성화) |
| 3 | TS (Task Switched) | 태스크 전환 시 FPU 상태 저장 트리거 |
| 4 | ET (Extension Type) | FPU 타입 식별용 (대부분 1로 고정) |
| 5 | NE (Numeric Error) | FPU 예외를 INT 16으로 내부 처리 |
| 16 | WP (Write Protect) | 커널 모드에서 read-only 페이지 보호 허용 |
| 18 | AM (Alignment Mask) | 정렬 예외 활성화 (CR4.AC 필요) |
| 29 | NW (Not Write-through) | 쓰기 동작 캐시 정책 제어 (write-through 금지) |
| 30 | CD (Cache Disable) | CPU 캐시 비활성화 |
| 31 | PG (Paging) | 페이징(가상 메모리 주소 변환) 활성화 |
PE (Protection Enable)
해당 값이 TRUE로 설정되면 보호 모드를 활성화합니다.
보호 모드에 대한 자세한 내용은 Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual에 설명되어 있습니다.

MP (Monitor Coprocessor)
EM (Emulation)
TS (Task Switched)
ET (Extension Type)
NE (Numeric Error)
WP (Write Protect)
AM (Alignment Mask)
NW (Not Write-through)
CD (Cache Disable)
PG (Paging)
페이징(가상 메모리 주소 변환)에 대한 활성화 여부입니다.
해당 값이 FALSE로 설정되면 모든 메모리는 물리 주소를 사용합니다.
CR1
현재 사용되고 있지 않은은 예약된 값입니다.
CR2
Page Fault가 발생한 메모리 주소를 나타냅니다. 페이지 폴트는 다음과 같은 경우에 발생합니다.
1. Access Violation
아래 예제에서는 NULL 주소에 엑세스하여 Page Fault가 발생합니다.
1
2
3
4
int* addr_value = NULL;
// Access Violation.
*addr_value = 123;
2. Protection Violation
아래 예제에서는 READONLY 메모리에 write를 시도하여 Page Fault가 발생합니다.
(‘static const’ 키워드로 변수를 선언하면 .rdata 섹션에 매핑됨)
1
2
3
4
static const value = 0; // .rdata (PAGE_READONLY)
// Protection Violation.
value = 123;
CR3
DirectoryTableBase의 물리 메모리 주소를 나타냅니다. DirBase를 통해 가상 메모리 주소를 물리 메모리 주소로 변환합니다.
CR4.LA57 설정에 따라 PML4 또는 PML5 페이징 방식이 적용됩니다.
해당 값은 PCB->DirectoryTableBase 값과 동일합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
14: kd> dt_eprocess ffffdf02ec514080 -r1
nt!_EPROCESS
+0x000 Pcb : _KPROCESS
+0x000 Header : _DISPATCHER_HEADER
+0x018 ProfileListHead : _LIST_ENTRY [ 0xffffdf02`ec514098 - 0xffffdf02`ec514098 ]
+0x028 DirectoryTableBase : 0x00000002`53ef0000
CR4
VMX, PAE, PML5 등 프로세서의 확장된 기능들을 제어합니다.
| Bit | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | VME (Virtual-8086 Mode Extensions) | V8086 모드에서 INT, POPF 등의 동작 허용 |
| 1 | PVI (Protected-Mode Virtual Interrupts) | 가상 인터럽트 플래그(IF) 사용 허용 |
| 2 | TSD (Time Stamp Disable) | 유저 모드에서 RDTSC 명령어 사용 금지 |
| 3 | DE (Debugging Extensions) | 고급 디버깅 기능 사용 허용 |
| 4 | PSE (Page Size Extension) | 4MB 페이지 (x86) 또는 1GB 페이지 (x64) 지원 |
| 5 | PAE (Physical Address Extension) | 36비트 이상 물리 주소 공간 지원 |
| 6 | MCE (Machine Check Enable) | CPU 하드웨어 오류 보고 기능 활성화 |
| 7 | PGE (Page Global Enable) | 전역 페이지 비트 사용 (TLB 성능 최적화) |
| 8 | PCE (Performance-Monitoring Counter Enable) | 유저 모드에서 RDPMC 허용 |
| 9 | OSFXSR | SSE 레지스터 저장용 FXSAVE/FXRSTOR 사용 허용 |
| 10 | OSXMMEXCPT | SSE 예외 처리 활성화 |
| 11 | UMIP (User-Mode Instruction Prevention) | 유저 모드에서 SGDT, SIDT, SMSW 등 금지 |
| 12 | LA57 | PML5 (5-Level-Paging) 활성화 |
| 13 | VMXE (VMX Enable) | 인텔 VT-x 하드웨어 가상화 활성화 |
| 14 | SMXE (SMX Enable) | 인텔 TXT/SMX 기능 활성화 |
| 16 | FSGSBASE | 유저 모드에서 RD/WR FSBASE, GSBASE 명령 허용 |
| 17 | PCIDE | CR3 기반 TLB 태그 기능 (Process Context ID) 활성화 |
| 18 | OSXSAVE | XGETBV, XSETBV 명령 및 AVX 컨텍스트 저장 허용 |
| 20 | SMEP (Supervisor Mode Execution Protection) | 커널에서 유저 모드 코드 실행 차단 |
| 21 | SMAP (Supervisor Mode Access Protection) | 커널에서 유저 모드 데이터 접근 차단 |
| 22 | PKE (Protection Key Enable) | 페이지 보호 키 기능 활성화 |
VME (Virtual-8086 Mode Extensions)
PVI (Protected-Mode Virtual Interrupts)
TSD (Time Stamp Disable)
DE (Debugging Extensions)
PSE (Page Size Extensions)
PAE (Physical Address Extension)
MCE (Machine Check Enable)
PGE (Page Global Enable)
PCE (Performance-Monitoring Counter Enable)
OSFXSR (FXSAVE/FXRSTOR Support)
OSXMMEXCPT (Unmasked SIMD Floating-Point Exceptions)
UMIP (User-Mode Instruction Prevention)
LA57 (5-Level Paging Enable)
PML5에 대한 활성화 여부입니다. 해당 값이 TRUE이면 PML5, FALSE이면 PML4 방식으로 페이징이 수행됩니다.
페이징은 CR4.LA57 뿐만 아니라 CR0.PG, CR4.PAE, IA32_EFER.LME 값도 함께 설정되어야 합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
5.5 4-LEVEL PAGING AND 5-LEVEL PAGING
Because the operation of 4-level paging and 5-level paging is very similar, they are described together in this
section. The following items highlight the distinctions between the two paging modes:
• A logical processor uses 4-level paging if CR0.PG = 1, CR4.PAE = 1, IA32_EFER.LME = 1, and CR4.LA57 = 0.
4-level paging translates 48-bit linear addresses to 52-bit physical addresses.13 Although 52 bits corresponds
to 4 PBytes, linear addresses are limited to 48 bits; at most 256 TBytes of linear-address space may be
accessed at any given time.
• A logical processor uses 5-level paging if CR0.PG = 1, CR4.PAE = 1, IA32_EFER.LME = 1, and CR4.LA57 = 1.
5-level paging translates 57-bit linear addresses to 52-bit physical addresses. Thus, 5-level paging supports a
linear-address space sufficient to access the entire physical-address space.