Model Specific Registers
MSR (Model Specific Registers)
IA-32 프로세서와 Intel 64 프로세서에는 MSR이라는 특수한 레지스터가 제공됩니다.
RDMSR, WRMSR 명령어를 통해 읽고 쓰기가 가능하며 다양한 하드웨어 기능들을 조회하거나 제어하는데 사용됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
11.4 MODEL-SPECIFIC REGISTERS (MSRS)
Most IA-32 processors (starting from Pentium processors) and Intel 64 processors contain a model-specific registers (MSRs). A given MSR may not be supported across all families and models for Intel 64 and IA-32 processors.
Some MSRs are designated as architectural to simplify software programming; a feature introduced by an architectural MSR is expected to be supported in future processors. Non-architectural MSRs are not guaranteed to be
supported or to have the same functions on future processors.
MSRs that provide control for a number of hardware and software-related features, include:
• Performance-monitoring counters (see Chapter 21, “Performance Monitoring”).
• Debug extensions (see Chapter 19, “Debug, Branch Profile, TSC, and Intel® Resource Director Technology
(Intel® RDT) Features”).
• Machine-check exception capability and its accompanying machine-check architecture (see Chapter 17,
“Machine-Check Architecture”).
• MTRRs (see Section 13.11, “Memory Type Range Registers (MTRRs)”).
• Thermal and power management.
• Instruction-specific support (for example: SYSENTER, SYSEXIT, SWAPGS, etc.).
• Processor feature/mode support (for example: IA32_EFER, IA32_FEATURE_CONTROL).
The MSRs can be read and written to using the RDMSR and WRMSR instructions, respectively.
When performing software initialization of an IA-32 or Intel 64 processor, many of the MSRs will need to be initialized to set up things like performance-monitoring events, run-time machine checks, and memory types for physical memory.
해당 명령은 커널 레벨에서만 사용 가능하며 사용 예시는 다음과 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
// Reads 64bit-width MSR
_Use_decl_annotations_ ULONG64 UtilReadMsr64(Msr msr) {
return __readmsr(static_cast<unsigned long>(msr));
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// See: BASIC VMX INFORMATION
// The first processors to support VMX operation use the write-back type.
const Ia32VmxBasicMsr vmx_basic_msr = {UtilReadMsr64(Msr::kIa32VmxBasic)};
if (static_cast<memory_type>(vmx_basic_msr.fields.memory_type) !=
memory_type::kWriteBack) {
HYPERPLATFORM_LOG_ERROR("Write-back cache type is not supported.");
return false;
}
RDMSR은 호출 시 전달하는 값에 따라 다른 정보를 반환하며 상세 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
IA32_VMX_BASIC
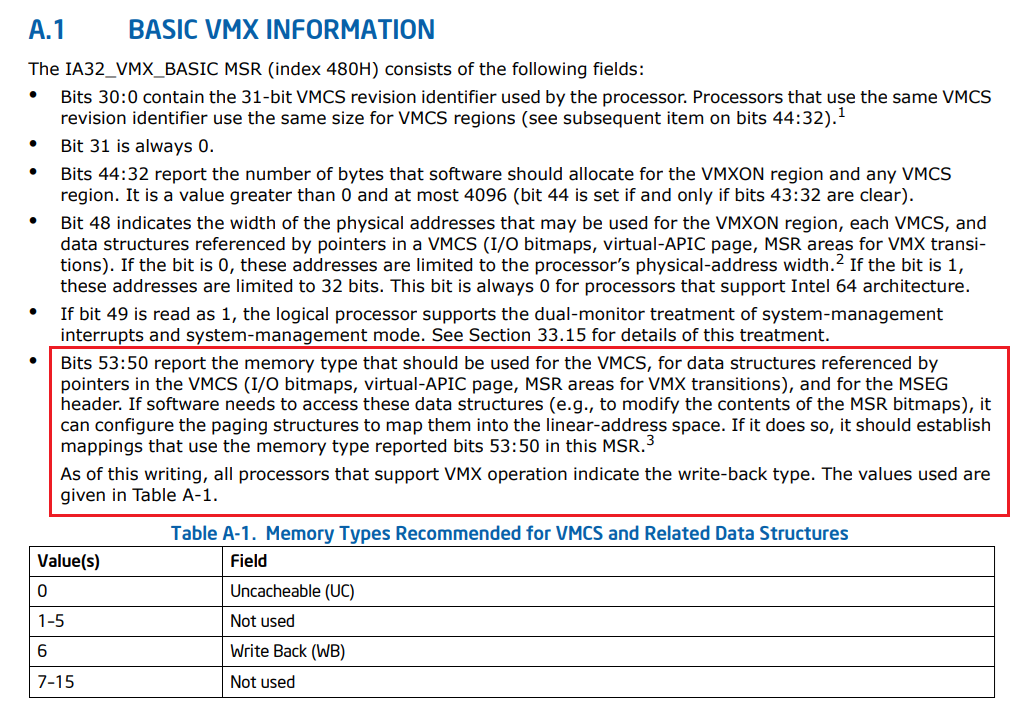
IA32_VMX_BASIC(480H)를 통해 반환되는 정보는 다음과 같습니다.
53:50 비트에 해당되는 값은 VMCS 및 참조되는 구조체에 대한 메모리 타입(Uncacheable, WriteBack)을 나타냅니다.
0:30 비트에 해당되는 값은 VMCS revision Identifier에 해당되며 VMXON region에 사용됩니다.
IA32_FEATURE_CONTROL
IA32_FEATURE_CONTROL(3A)은 VMX 기능을 활성화하고 조회하는데 사용됩니다.
하이퍼바이저를 실행하기 위해서는 CR4.VMXE 비트를 1으로 설정하고, MSR을 통해 VMX(VMXON)을 활성화해야 합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
24.7 ENABLING AND ENTERING VMX OPERATION
Before system software can enter VMX operation, it enables VMX by setting CR4.VMXE[bit 13] = 1. VMX operation
is then entered by executing the VMXON instruction. VMXON causes an invalid-opcode exception (#UD) if executed
with CR4.VMXE = 0. Once in VMX operation, it is not possible to clear CR4.VMXE (see Section 24.8). System software leaves VMX operation by executing the VMXOFF instruction. CR4.VMXE can be cleared outside of VMX operation after executing of VMXOFF.
VMXON is also controlled by the IA32_FEATURE_CONTROL MSR (MSR address 3AH). This MSR is cleared to zero
when a logical processor is reset.
0비트에 해당되는 값은 VMX에 대한 잠금 기능입니다. 해당 값을 1로 변경한 경우 VMX가 활성화된 것을 의미합니다.
해당 비트를 1으로 변경한 경우 프로세서가 리셋되기 전까지 WRMSR을 통해 값을 다시 변경할 수 없습니다.

1, 2비트에 해당되는 값은 VMXON에 대한 활성화 기능입니다. BIOS 화면에서 설정이 가능하며 인텔에서는 0비트와 함께 설정을 요구하고 있습니다.
1비트는 SMX, 2비트는 Non-SMX 환경을 의미합니다. 대부분의 하이퍼바이저에서는 2비트를 활성화해야 동작합니다.

IA32_VMX_EPT_VPID_CAP
IA32_VMX_EPT_VPID_CAP(48CH)은 EPT와 VPID에 대한 지원 여부를 나타냅니다.
